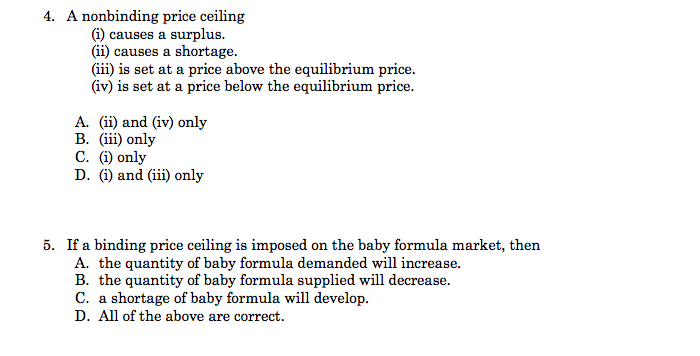This is something i would explain and illustrate with students in my economics microeconomics classes.
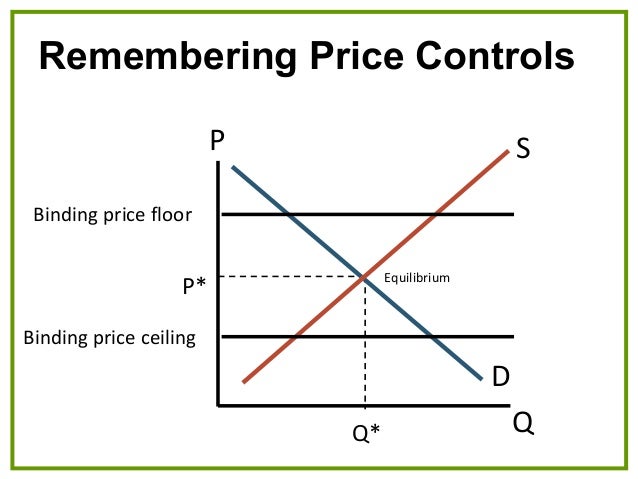
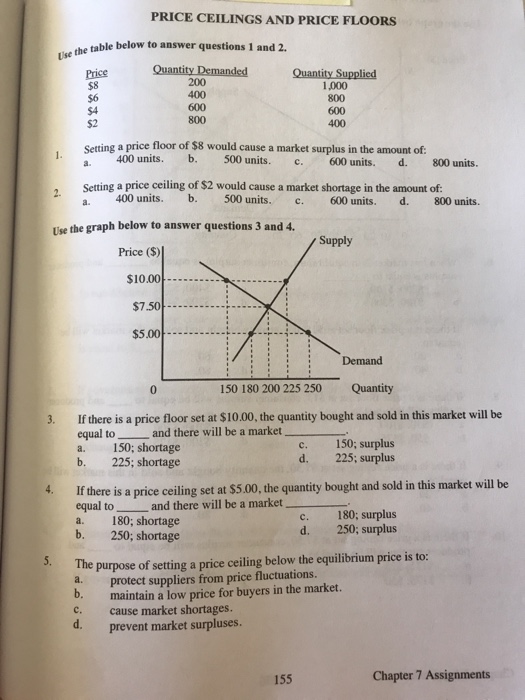
Price ceilings cause shortages and price floors cause surpluses.
Suppose that the supply and demand for wheat flour are balanced at the current price and that the government then fixes a lower maximum price.
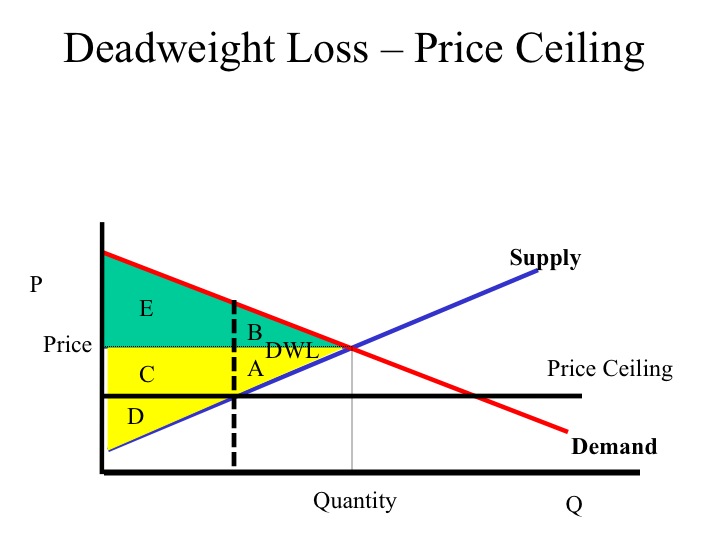
However price ceiling in a long run can cause adverse effect on market and create huge market inefficiencies.
A price ceiling causes an increase in demand if the ceiling price is set below the equilibrium price d.
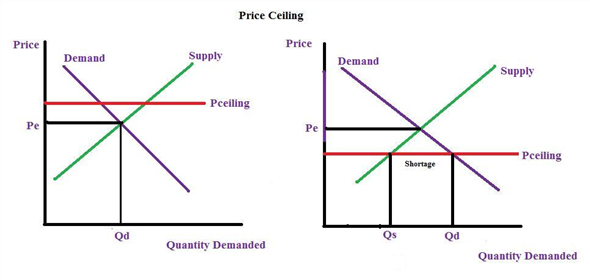
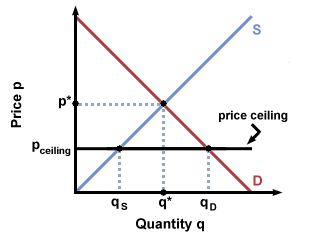
A price ceiling is designed to protect consumers from prices that are too high so to protect consumers the government sets a maximum price.
Is quantity demanded or quantity supplied greater.
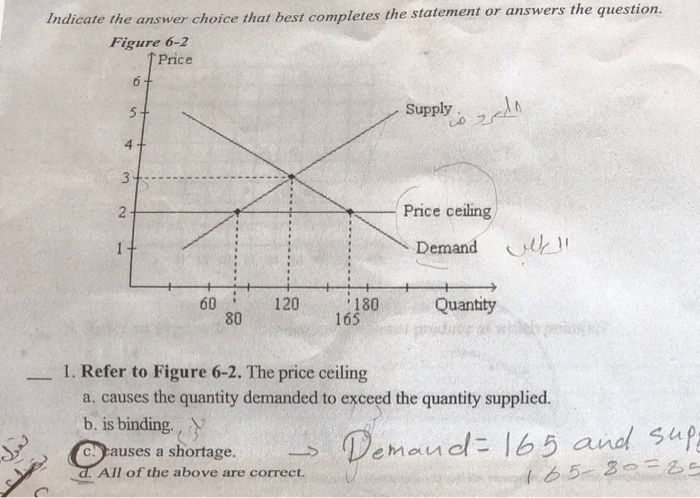
A price ceiling set below the equilibrium price causes a surplus.
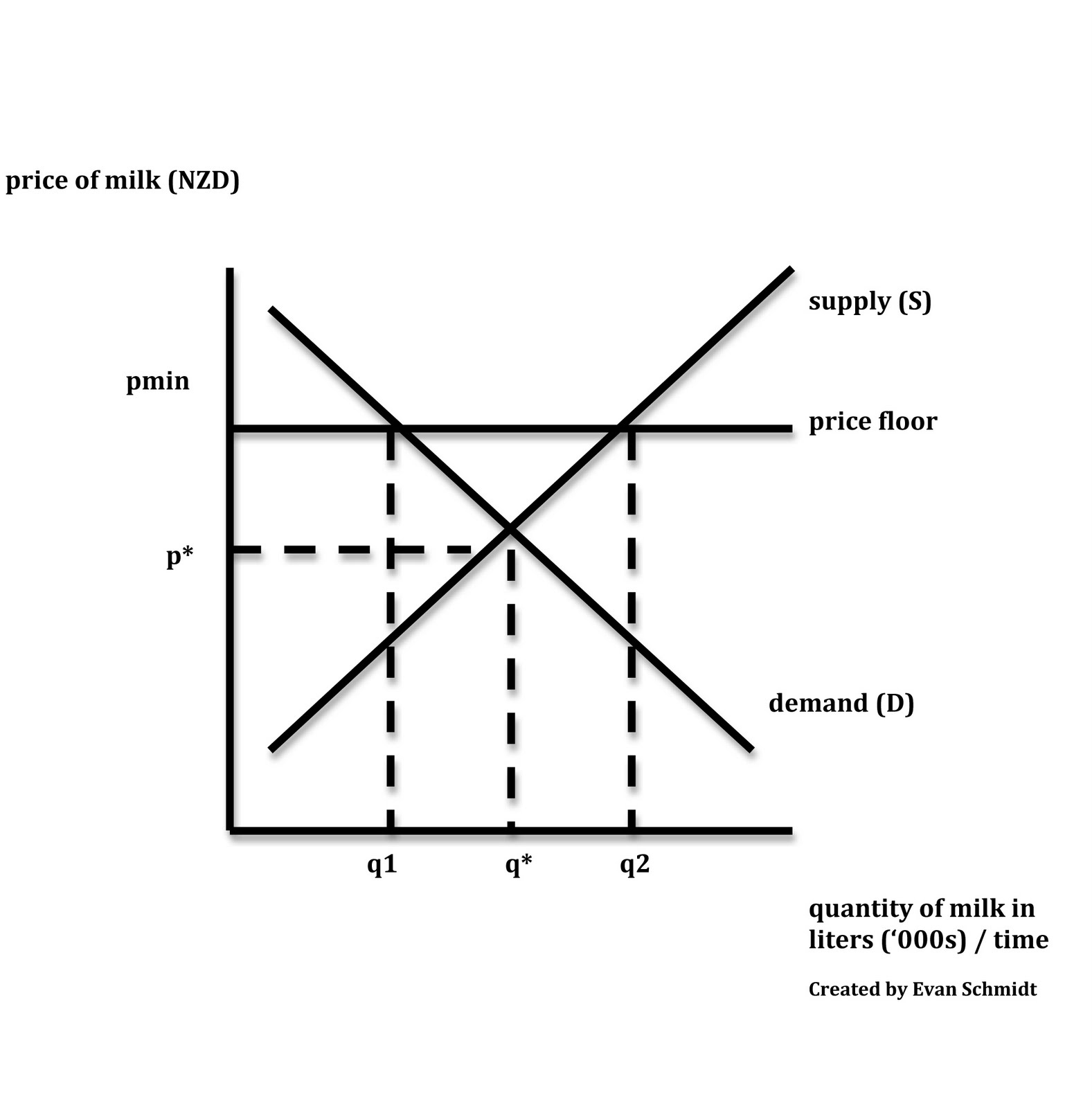
A price floor can cause a surplus while a price ceiling can cause a shortage but not always.
They are forced to pay higher prices and consume smaller quantities than they would with free market.
A price ceiling that is not a binding constraint today could cause a shortage in the future if demand were to increase and raise the equilibrium price above the fixed price ceiling.
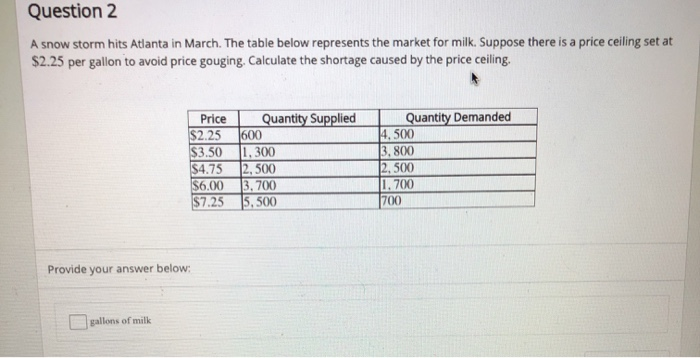
One way shortages occur is through a price ceiling.
Price ceilings which prevent prices from exceeding a certain maximum cause shortages.
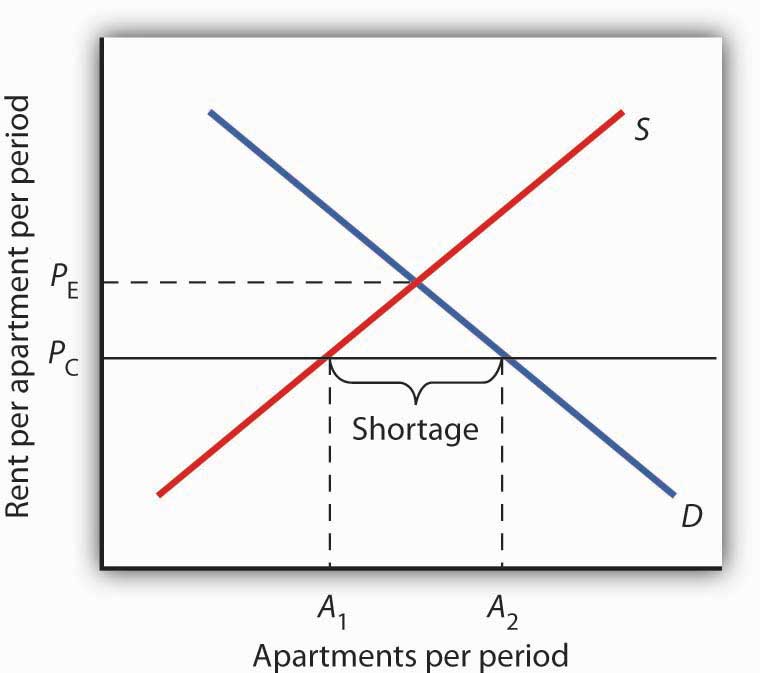
Imagine if you had to rent out the front apartment of the farm for half of what you wanted to rent because of some new law obama made.
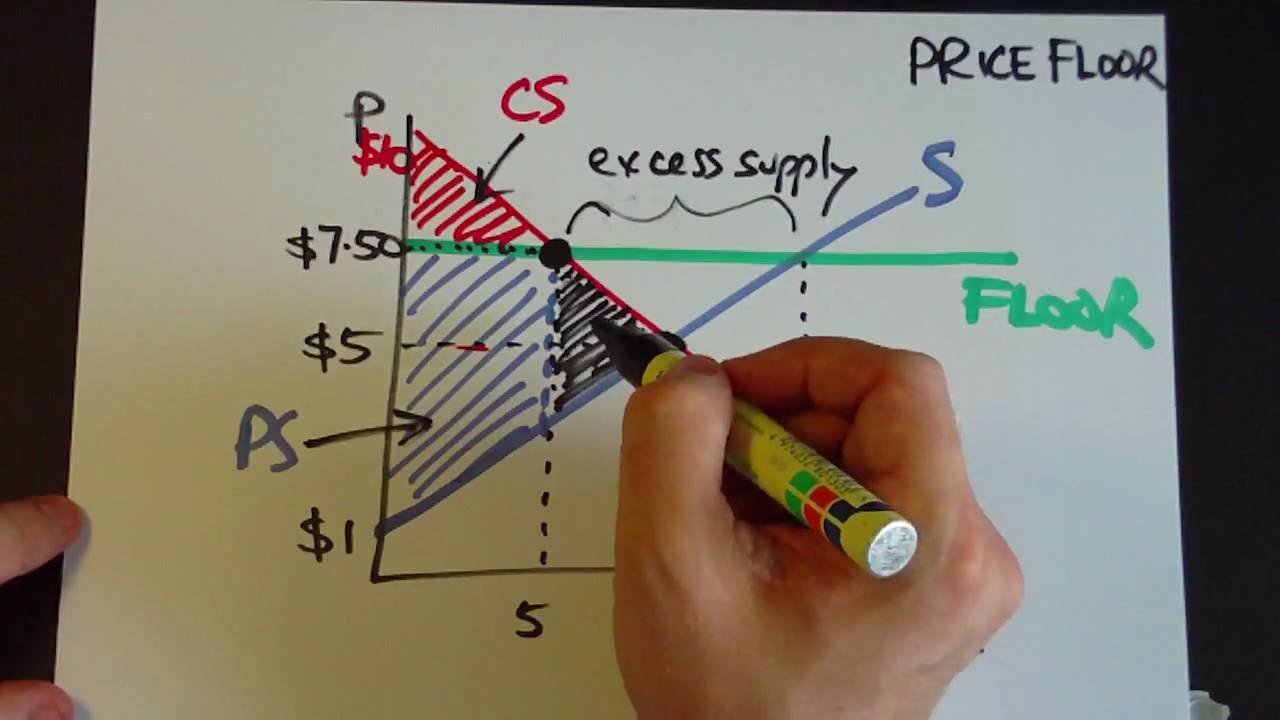
Price floors cause surpluses.
A price floor causes a surplus if the price floor is below the equilibrium price c.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Interfere with the rationing function of prices.
Shift demand and supply curves and therefore have no effect on the rationing function of prices.
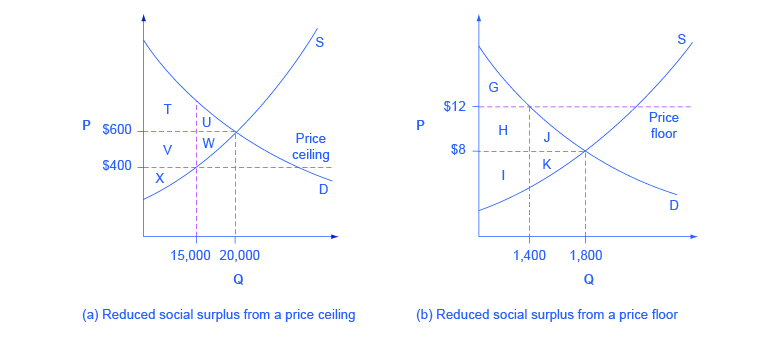
If the market price is above the equilibrium price quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded creating a surplus.
It creates surplus only if the floor is set above the equilibrium price.
But the price floor p f blocks that communication between suppliers and consumers preventing them from responding to the surplus in a mutually appropriate way.
Some effects of price ceiling are.
The supply of.
An example of a price ceiling we can use to explain the concept would be rent control.
Price floors transfer consumer surplus to producers.
A price ceiling causes a shortage if the ceiling price is above the equilibrium price b.
A shortage happens when there is more of a demand for a good than there is supplied.
Suppliers can be worse off.
Cause surpluses and shortages respectively.
Price ceilings cause shortages.
Make the rationing function of free markets more efficient.
If price ceiling is set above the existing market price there is no direct effect.
Consumers are clearly made worse off by price floors.